The past, present and... future?
For decades, plug & perf ("PNP") was the only generally accepted method to achieve multistage fracturing. At the turn of the century, ball operated sliding sleeves ("BOSS") were introduced. BOSS opened sequentially from toe to heel. The ball served two functions: 1. To open the sleeve and 2. To isolate previously treated sleeves. To selectively open the sleeves, ball and seat sizes were varied, starting with the smallest in the toe and gradually increasing towards the heel.
The number of sleeves that could be operated was increased through the invention of 'multi-sleeves,' where a single ball could open a set of sleeves with matching seat dimensions. BOSS was essentially emulating PNP stages with multiple entry points, except that they were typically uncemented due to the inability to pump a cement wiper dart through dozens of tiny restrictions. The BOSS technique worked great for wells with limited lateral length and wide fracture spacing and as such, use of BOSS saw a significant increase from 2010 through 2015.
A third technique called coiled tubing annular frac ("CTAF") was introduced almost ten years ago. This was a game-changer in terms of proppant placement. Coiled tubing shifts open one sliding sleeve at a time and directs proppant down the CT annulus into the single entry point. While this proved excellent at propping 100% of the fractures, most operators in the lower 48 states ("L48") struggle to accept the added risk of pumping enormous volumes of proppant at high rate down the CT annulus. CTAF remains a popular treatment method in Canada but has not gained traction in L48.
"When we start to see a drop in production for each dollar spent, we need to stop what we're doing and reevaluate our options!" |
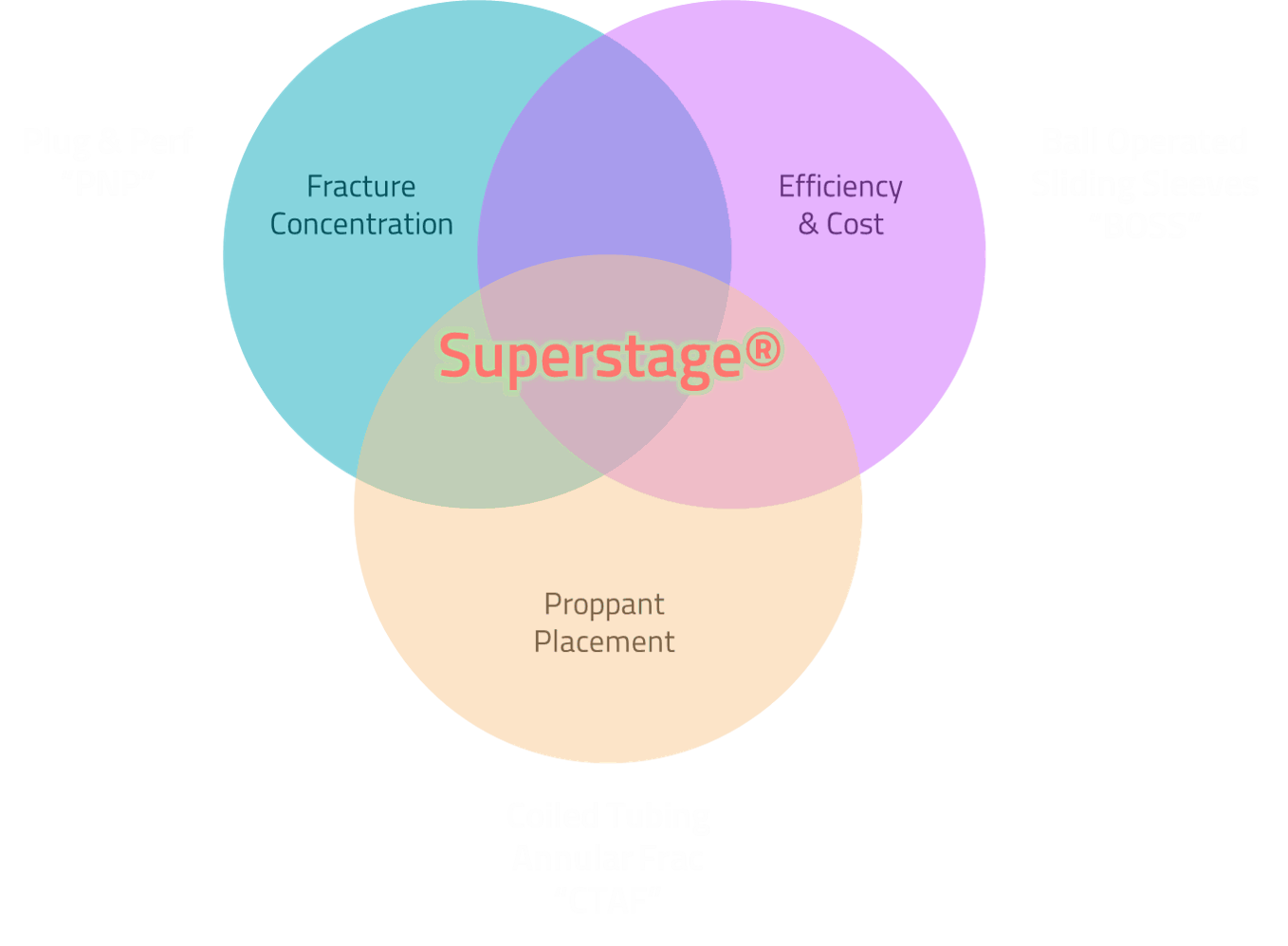
Superstage® Pinpoint Stimulation ("SPS") offers the fracture concentration of PNP, the efficiency of BOSS and the diversion control of CTAF. Contact Entech for an opportunity to pilot the technology in your field.
References
Jo, H. (2012, January 1). Optimizing Fracture Spacing to Induce Complex Fractures in a Hydraulically Fractured Horizontal Wellbore. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/154930-MS
Jacobs, T. (2016, June 1). EOR-For-Shale Ideas to Boost Output Gain Traction. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/0616-0028-JPT
Wheaton, B., Haustveit, K., Deeg, W., Miskimins, J., & Barree, R. (2016, February 1). A Case Study of Completion Effectiveness in the Eagle Ford Shale Using DAS/DTS Observations and Hydraulic Fracture Modeling. Society of Petroleum Engineers. doi:10.2118/179149-MS